Inspirating Info About What Controls PWM Fan Speed

Unlocking the Secrets of PWM Fan Speed Control
1. The Symphony of Silence (or Roar!)
Ever wondered how your computer manages to keep its cool, both literally and figuratively? It's all thanks to those little whirring wonders we call fans! But how does your PC intelligently adjust their speed, keeping things quiet when you're just browsing and cranking them up when you're gaming hard? The key is a technology called PWM, or Pulse Width Modulation. It's a bit like a dimmer switch for your fans, giving you precise control over their performance.
Think of it like this: Imagine you're trying to explain to someone how often to blink. Instead of saying "blink constantly," or "never blink," you can say, "blink for a short duration, with a specific frequency." PWM does something similar. It sends electrical pulses to the fan, turning it on and off rapidly. The width of these pulses determines how much power the fan receives, and thus, how fast it spins. Pretty neat, huh?
The beauty of PWM lies in its efficiency and precision. Older fan control methods simply reduced the voltage sent to the fan, which could lead to inconsistent performance and even cause some fans to stall at low speeds. PWM, on the other hand, delivers full voltage in short bursts, ensuring smooth and reliable operation across a wide range of speeds. This translates to better cooling performance, quieter operation, and a longer lifespan for your fans.
So, next time you hear your computer fans speeding up, remember the magic of PWM at work. It's the unsung hero of PC cooling, silently toiling away to keep your components happy and your gaming sessions uninterrupted. It is all about what controls PWM fan speed.

Arduino Fan Control Using High Frequency 25kHz PWM // 4Wire CPU Fans
The Brains Behind the Operation
2. Who's the Boss?
Okay, so we know PWM is the how, but what's the who? Who decides when to speed up or slow down the fans? The answer usually lies with your motherboard, or a dedicated fan controller if you're a serious enthusiast. These components act as the brains of the operation, constantly monitoring the temperature of various components within your PC.
Most modern motherboards have built-in sensors that track the temperature of the CPU, GPU, and other critical components. When the temperature reaches a certain threshold, the motherboard sends a signal to the PWM fan, instructing it to increase its speed. Conversely, when the temperature drops, the fan slows down. It's a constant balancing act, ensuring that your components stay within a safe operating range.
Fan controllers offer even more granular control over fan speeds. They often come with their own temperature sensors and software, allowing you to customize fan curves and create specific cooling profiles for different scenarios. For example, you might create a profile that prioritizes silence during normal desktop use and another that prioritizes maximum cooling during gaming.
The communication between the motherboard (or fan controller) and the PWM fan happens through the 4-pin connector that you see on your fans. Two of these pins are for power and ground, one is for sensing fan speed (so the motherboard knows how fast the fan is actually spinning), and the crucial fourth pin is the PWM signal pin, which carries the instructions to control the fan's speed. Clever, right?

Understanding Fan Curves and Customization
3. Tuning for Optimal Performance
Now that you know who's in charge, let's talk about how you can take control yourself! Most motherboards and fan controllers allow you to customize "fan curves." A fan curve is essentially a graph that maps temperature to fan speed. You can use this to define how your fans respond to different temperature levels.
For instance, you might set the fan speed to 20% until the CPU reaches 50 degrees Celsius, then gradually increase the speed to 100% as the temperature rises to 80 degrees Celsius. This allows you to fine-tune the balance between noise and cooling performance to your liking. Many software utilities provide visual interfaces for creating and editing fan curves, making the process relatively straightforward.
Experimenting with fan curves is a great way to optimize your system's cooling performance and reduce noise levels. It's worth taking the time to find a configuration that works best for your specific needs and hardware. Keep an eye on your component temperatures while you're tweaking things to ensure that you're not sacrificing cooling for silence.
Some software even allows you to create different profiles for different applications. Imagine having a silent profile for browsing and a high-performance profile for gaming, switching automatically based on what you're doing! The possibilities are endless — limited only by your patience and willingness to experiment.

Troubleshooting PWM Fan Issues
4. When Things Go Wrong
Even with the best technology, things can occasionally go wrong. If your PWM fans aren't behaving as expected, here are a few things to check:
First, make sure that your fans are properly connected to the correct 4-pin headers on your motherboard or fan controller. Sometimes, accidentally plugging a PWM fan into a 3-pin header can cause it to run at full speed or not work at all. Double-check the connections and consult your motherboard manual if you're unsure.
Second, verify that PWM control is enabled in your BIOS or UEFI settings. Some motherboards have options to switch between PWM and voltage control, and you'll want to make sure PWM is selected. Also, ensure that your fan curves are configured correctly and that they're actually being applied. Sometimes, software glitches can prevent fan curves from working as intended.
Finally, if you're still having problems, consider testing your fans with a different motherboard or fan controller to rule out any hardware issues. A faulty fan, motherboard header, or fan controller can all cause unexpected behavior. A simple swap can help you pinpoint the source of the problem.
Also, keep an eye on dust buildup. Dust can impede fan performance, causing them to spin faster and louder to compensate. Regular cleaning can help keep your fans running smoothly and quietly.
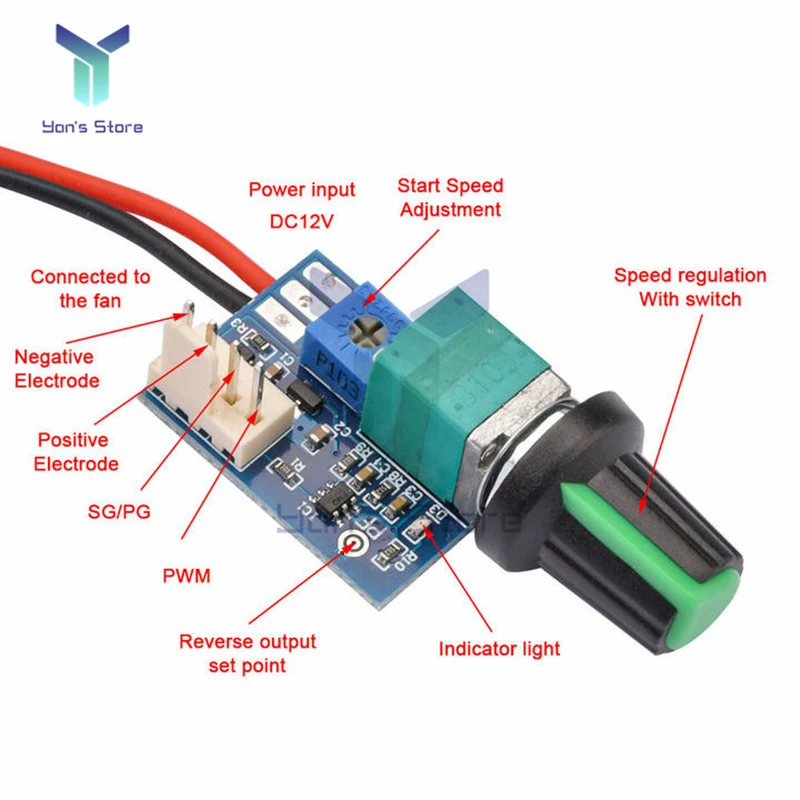
DC12VAdjustable0100PWMFanSpeedControllerwithKnobSwitch4
Beyond the Basics
5. Taking it to the Next Level
For the true enthusiast, there's always more to explore! Some advanced fan controllers offer features like individual fan control, allowing you to fine-tune the speed of each fan independently. This can be particularly useful for systems with multiple fans, where you might want to prioritize cooling for specific components.
Another advanced technique is using external temperature sensors to control fan speeds. Instead of relying solely on the motherboard's built-in sensors, you can place external sensors directly on components like the VRMs or RAM to get more accurate temperature readings and create more responsive fan curves. This can lead to even better cooling performance and lower noise levels.
Finally, some users experiment with custom water cooling loops and sophisticated software to create elaborate cooling systems with highly customized fan profiles. These setups often involve monitoring coolant temperature and adjusting fan speeds based on the overall thermal load of the system. It's a rabbit hole, but a fun one for those who enjoy tinkering and optimizing their hardware.
The world of PWM fan control is surprisingly deep and complex. From basic motherboard control to advanced custom loops, there's always something new to learn and experiment with. It's all about finding the right balance between cooling performance, noise levels, and personal preference.
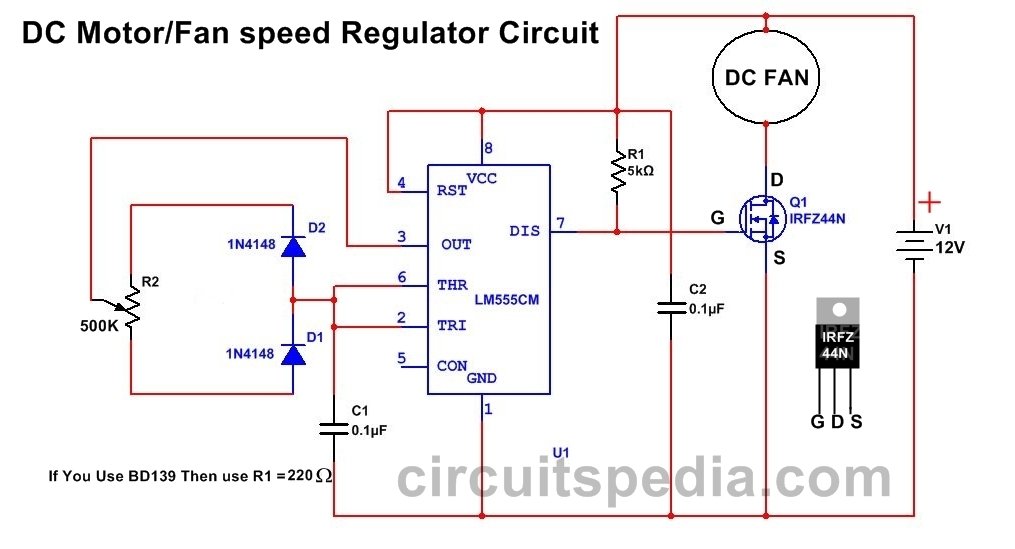
12v DC FAN Motor Speed Controller Regulator Circuit Diagram
FAQ
6. Your Burning Questions Answered
Q: What's the difference between a 3-pin and a 4-pin fan?
A: 3-pin fans are voltage controlled, meaning their speed is adjusted by changing the voltage supplied to them. 4-pin fans are PWM controlled, allowing for more precise speed adjustments through pulse width modulation. 4-pin fans are generally preferred for better control and quieter operation.
Q: Can I use a 4-pin fan on a 3-pin motherboard header?
A: Yes, you can! The fan will run, but it will likely run at full speed all the time because it won't be able to receive the PWM signal. Some motherboards may offer voltage control on 3-pin headers, which would allow you to adjust the fan speed, but it won't be as precise as PWM control.
Q: My PWM fan is running at full speed all the time. What could be the problem?
A: Several things could be causing this. Check that PWM control is enabled in your BIOS/UEFI. Ensure the fan is plugged into a 4-pin header. Update your motherboard drivers, as sometimes outdated drivers can cause issues. You can also check the fan speed in the BIOS. If the PWM signal is not sending properly, it can run full speed all the time.